Question: As blood pressure increases, the volume of blood returned to the left ventricle will increase, stretching it more than typical, leading to an increase in stroke volume. This is an example of cardiac reserve contractility preload afterload cardiac output.
What does stretching of the ventricles lead to?
Stretching of the myocardium of the ventricles during ventricular diastole is referred to as preload. An increase in preload leads to an increased force of contraction in the ventricle.
What is the stretch on the ventricles prior to contraction?
Preload is the force that stretches the cardiac muscle prior to contraction. This force is composed of the volume that fills the heart from venous return. Due to the molecular arrangement of actin and myosin in muscle, the more the incoming venous volume stretches the muscle, the further it will contract.
What is the Frank Starling effect?
6 What is the Frank-Starling law? The Frank-Starling law states that the force or tension developed in a muscle fiber depends on the extent to which the fiber is stretched. In a clinical situation, when increased quantities of blood flow into the heart (increasing preload), the walls of the heart stretch.
What happens when left ventricular pressure increases?
The LV pressure increases without a change in volume during isovolumetric contraction. When the LV pressure exceeds the aortic pressure, the aortic valve opens. During LV ejection, LV volume falls. LV ejection terminates with closure of the aortic valve.
What causes left ventricle dilation?
The cause of dilated cardiomyopathy often isn't known. Up to one-third of the people who have it inherit it from their parents. Some diseases, conditions and substances also can cause the disease, such as: Coronary heart disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, diabetes, thyroid disease, viral hepatitis and HIV.
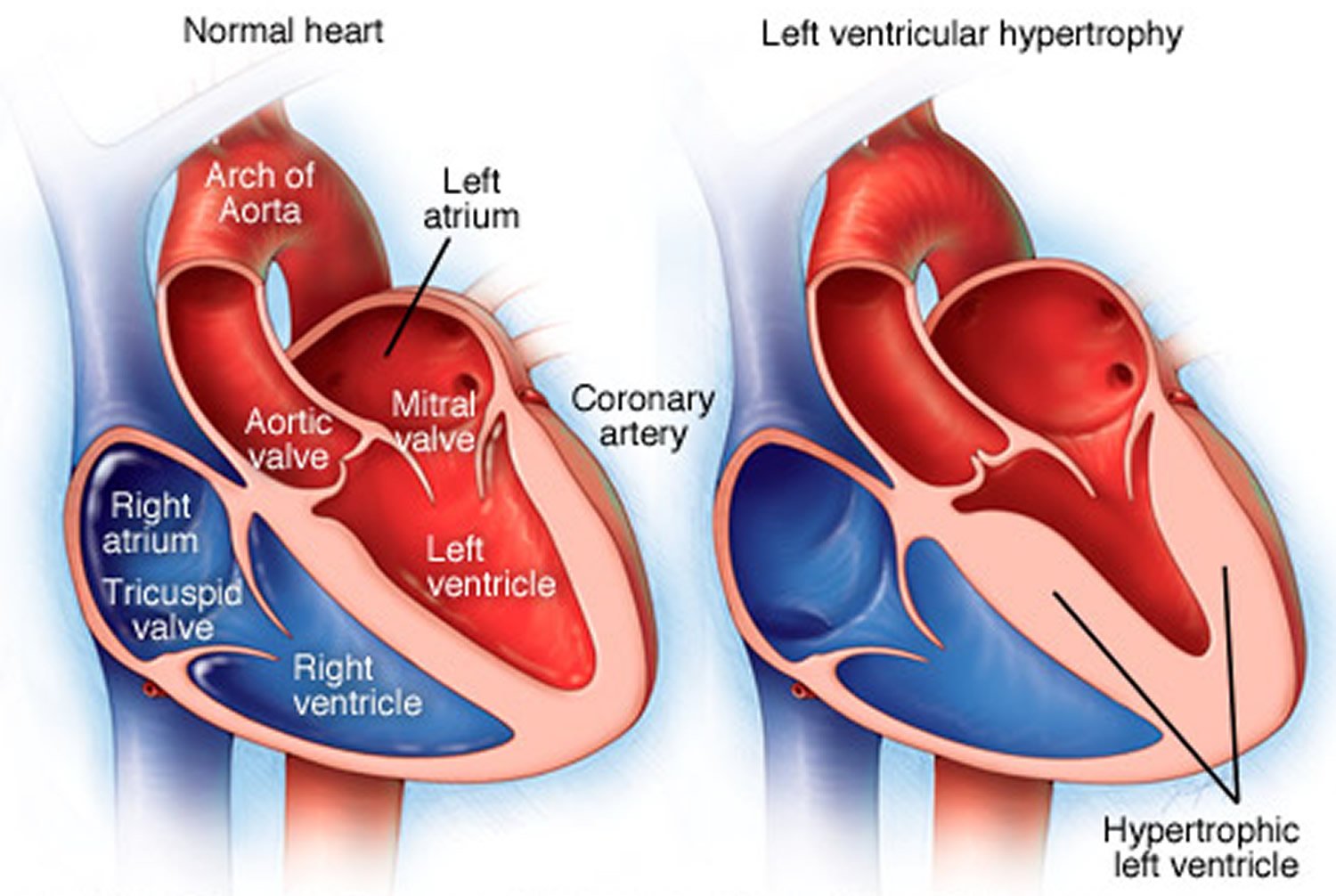
What happens when the heart is stretched?
In dilated cardiomyopathy the muscle walls of the heart become stretched and thin, so they cannot squeeze (contract) properly to pump blood around the body.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes the left ventricle to weaken?
The most common cause of left-sided heart failure is caused by heart related diseases such as coronary artery disease (CAD) or a heart attack. Other left ventricular failure causes can include: Cardiomyopathy. Cocaine use.
What is left ventricular wall thinning?
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the left ventricle, the heart's main pumping chamber, is enlarged (dilated). As the chamber gets bigger, its thick muscular wall stretches, becoming thinner and weaker. This affects the heart's ability to pump enough oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body.
FAQ
- What happens if there is an increased stretch to the baroreceptors above normal?
- Stretching of the baroreceptors as a result of increased blood pressure causes an increase in the activity of the vagal nerve by projection to the nucleus ambiguus. It also causes inhibition of the sympathetic outflow from the RVLM, ultimately leading to decreased heart rate and blood pressure.
- What is the basic function of hydrostatic pressure?
- The hydrostatic pressure in the intravascular space (Pc) is the principle force driving water and electrolytes out of the capillary into the interstitial space. The filtration force of the capillary hydrostatic pressure is opposed by the tissue pressure surrounding the capillaries (Pt).
When an increase of blood in the left ventricle causes stretching of the ventricle, the heart:
| What causes receptors in the heart to be stretched? | As venous return increases, the pressure in both superior and inferior vena cava increase. This results is an increase in the pressure of the right atrium, which stimulates the atrial stretch receptors. |
| When an increase of blood in the left ventricle causes stretching of the ventricle the heart | Dilated cardiomyopathy is a type of heart muscle disease that causes the heart chambers (ventricles) to thin and stretch, growing larger. |
- When an increase of blood in the left ventricle causes stretching of the ventricle, the heart
- By J King · 2022 · Cited by 55 — Greater end-diastolic volumes of blood returned to the heart, increase the passive stretching of the heart muscles. This in turn results in the ventricles
- What is a lvh cardio
- Sep 24, 2022 — Left ventricular hypertrophy is a thickening of the wall of the heart's main pumping chamber. This thickening may result in elevation of

